Specific heat is the heat capacity of a material that it absorbs to raise the temperature by one degree Celsius. In case of concrete, it is the heat capacity of concrete. Specific heat is measured in joules per kg per degree Celsius. Mineral properties of aggregates affect the specific heat of concrete. Specific heat increases with an increase in moisture content of the concrete. it also increases with an increase in concrete temperature.
Specific heat gets affected by the density of concrete. With an increase in concrete density, specific heat decreases. This is so because when density increases then voids become less in concrete and hence little area is available for absorbing heat.
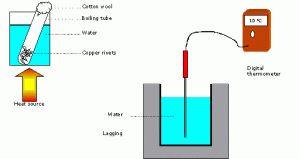
If excess heat comes in contact with concrete then concrete may crack. A range of the specific heat for a normal concrete lies between 840 to 1170 j/kg per centigrade. For determining specific heat elementary physics methods are used. As shown below